Template Strands
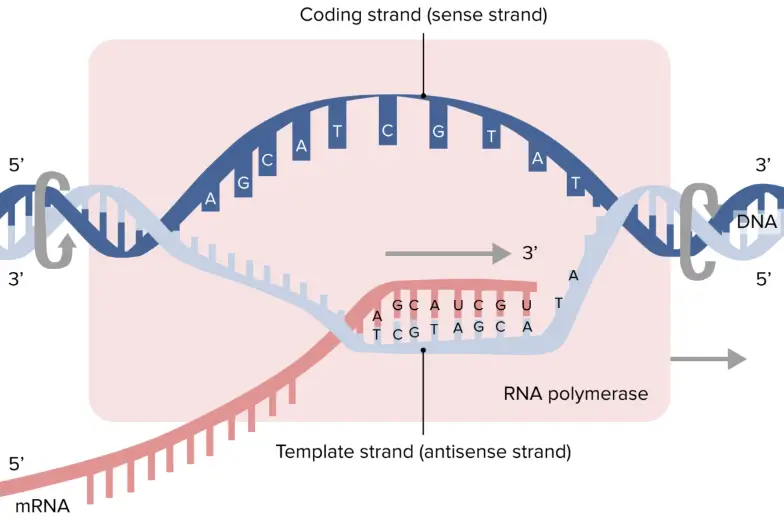
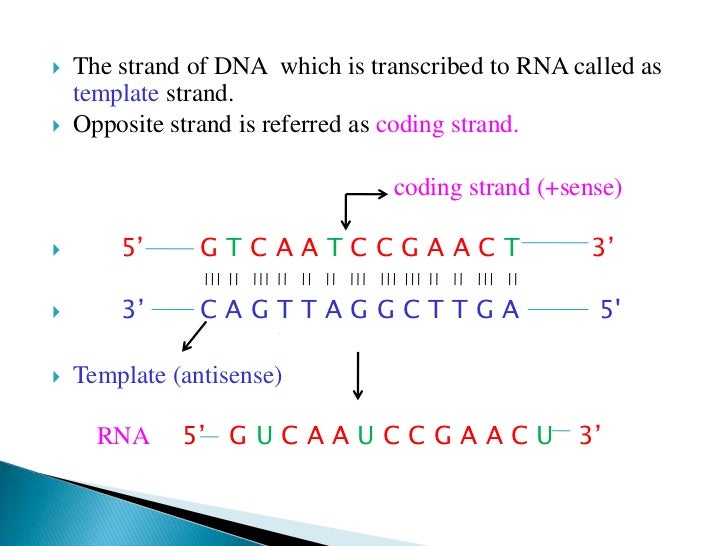
Template Strands - The template strand goes in one direction, while the coding strand goes in the opposite direction. In the process of making mrna for protein synthesis, dna's two strands are divided into either template strands or coding strands. The template strand, also known as the antisense strand, is the strand of dna that serves as a template for the synthesis of a complementary rna molecule. The coding strand of dna is the strand that codes for the gene of interest. What is the template strand? Understanding the coding and template strands is crucial in comprehending dna replication and gene expression. What is the difference between coding strand and template strand? The coding and template strands are. A dna template strand generally refers to the strand which is used by the enzyme dna polymerases and rna polymerases to attach with the. On the other hand, the template strand, also known as the antisense strand, serves as a template for rna synthesis during transcription. On the other hand, the template strand, also known as the antisense strand, serves as a template for rna synthesis during transcription. The coding strand of dna is the strand that codes for the gene of interest. The template contains anticodons, while coding involves codons. Understanding the coding and template strands is crucial in comprehending dna replication and gene expression. Understanding the distinction between template and coding strands of dna is fundamental for appreciating genetic transcription. What is dna template strand? The coding strand does not. These two strands play distinct but. The template strand is the single strand of dna that serves as a guide for the synthesis of a complementary strand during processes like dna replication and transcription. What is the difference between coding strand and template strand? The template strand goes in one direction, while the coding strand goes in the opposite direction. The template strand is one of the dna strands whose base sequence helps in building mrna through complementary base sequencing. The template strand, also known as the antisense strand, is the strand of dna that serves as a template for the synthesis of a. The difference between the template and coding strand of dna is that the template strand contains information for protein synthesis. The coding and template strands are. The dna strand known as the template strand serves as a blueprint for the. In the process of making mrna for protein synthesis, dna's two strands are divided into either template strands or coding. Its two essential strands, the coding strand and the template strand. On the other hand, the template strand, also known as the antisense strand, serves as a template for rna synthesis during transcription. The template strand, also known as the antisense strand, is the strand of dna that serves as a template for the synthesis of a complementary rna molecule.. The coding strand does not. The coding and template strands are. The template strand, also known as the antisense strand, is the strand of dna that serves as a template for the synthesis of a complementary rna molecule. What is the template strand? The template strand, or antisense strand,. The template strand goes in one direction, while the coding strand goes in the opposite direction. What is dna template strand? The template contains anticodons, while coding involves codons. The template strand is one of the dna strands whose base sequence helps in building mrna through complementary base sequencing. The coding strand of dna is the strand that codes for. These two strands play distinct but. The template strand, or antisense strand,. Its two essential strands, the coding strand and the template strand. What is dna template strand? In this blog post, we will explore an intriguing aspect of dna: In the process of making mrna for protein synthesis, dna's two strands are divided into either template strands or coding strands. What is dna template strand? The template strand, also known as the antisense strand, is the strand of dna that serves as a template for the synthesis of a complementary rna molecule. The template strand serves as a. Understanding. The template strand is the single strand of dna that serves as a guide for the synthesis of a complementary strand during processes like dna replication and transcription. A dna template strand generally refers to the strand which is used by the enzyme dna polymerases and rna polymerases to attach with the. On the other hand, the template strand, also. The coding strand does not. The dna strand known as the template strand serves as a blueprint for the. Understanding the distinction between template and coding strands of dna is fundamental for appreciating genetic transcription. What is the difference between coding strand and template strand? The template strand serves as a. In the process of making mrna for protein synthesis, dna's two strands are divided into either template strands or coding strands. The template strand is one of the dna strands whose base sequence helps in building mrna through complementary base sequencing. The coding and template strands are. What is the difference between coding strand and template strand? The difference between. These two strands play distinct but. What is the difference between coding strand and template strand? The template strand, or antisense strand,. The template strand, also known as the antisense strand, is the strand of dna that serves as a template for the synthesis of a complementary rna molecule. Understanding the distinction between template and coding strands of dna is fundamental for appreciating genetic transcription. The template contains anticodons, while coding involves codons. Understanding the coding and template strands is crucial in comprehending dna replication and gene expression. The template strand is one of the dna strands whose base sequence helps in building mrna through complementary base sequencing. The coding and template strands are. The template strand serves as a. In the process of making mrna for protein synthesis, dna's two strands are divided into either template strands or coding strands. The dna strand known as the template strand serves as a blueprint for the. A dna template strand generally refers to the strand which is used by the enzyme dna polymerases and rna polymerases to attach with the. What is the template strand? The coding strand of dna is the strand that codes for the gene of interest. The template strand is the single strand of dna that serves as a guide for the synthesis of a complementary strand during processes like dna replication and transcription.Which Strand Is The Template Strand
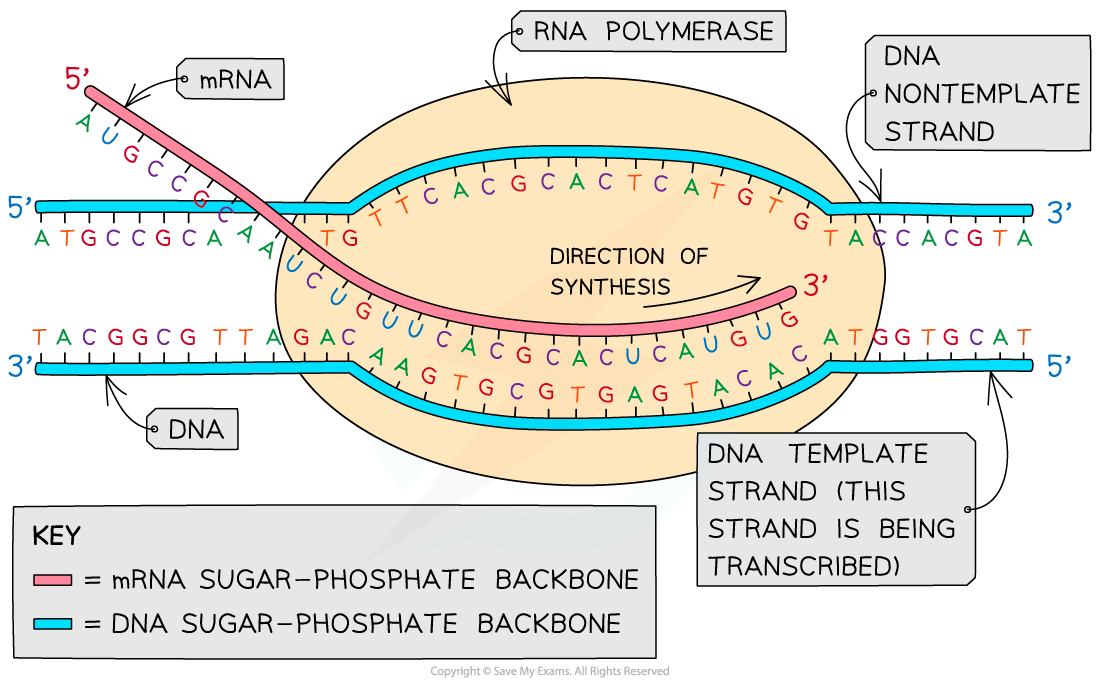
Key Components Of Gene Transcription Diagram Transcription D
What Is A Template Strand
Dna Coding And Template Strands
Coding Strand vs. Template Strand 6 Key Differences
Dna Coding And Template Strands
What Is The Template Strand, The template strand acts as a base for
What Is The Template Strand
AQA A Level Biology复习笔记4.2.3 Transcription翰林国际教育
Template Strand Vs Coding Strand Understanding The Difference GRAPHICOLD
On The Other Hand, The Template Strand, Also Known As The Antisense Strand, Serves As A Template For Rna Synthesis During Transcription.
On The Other Hand, Template Strands, Also Known As Antisense Strands, Act As The Complementary Partner To Coding Strands During Dna Replication And Transcription.
The Template Strand Goes In One Direction, While The Coding Strand Goes In The Opposite Direction.
The Coding Strand Does Not.
Related Post: