Java Allocate Memory For Template Array
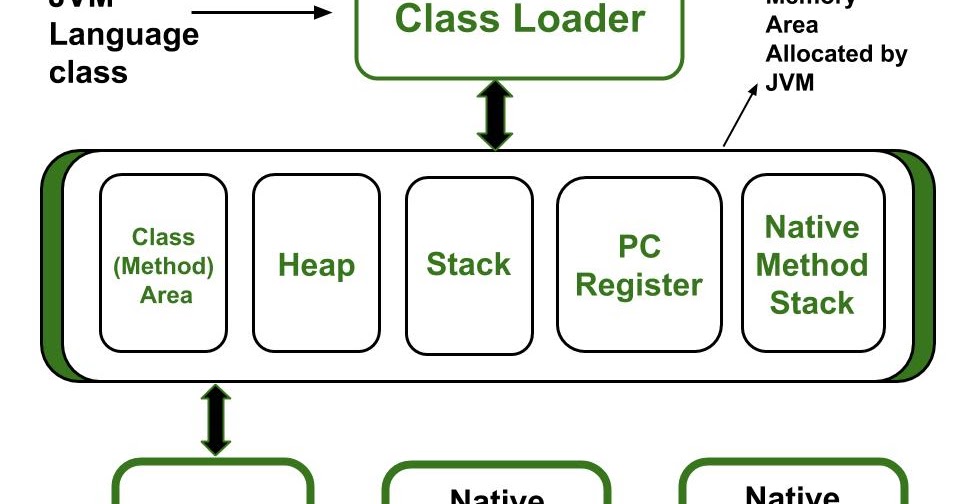
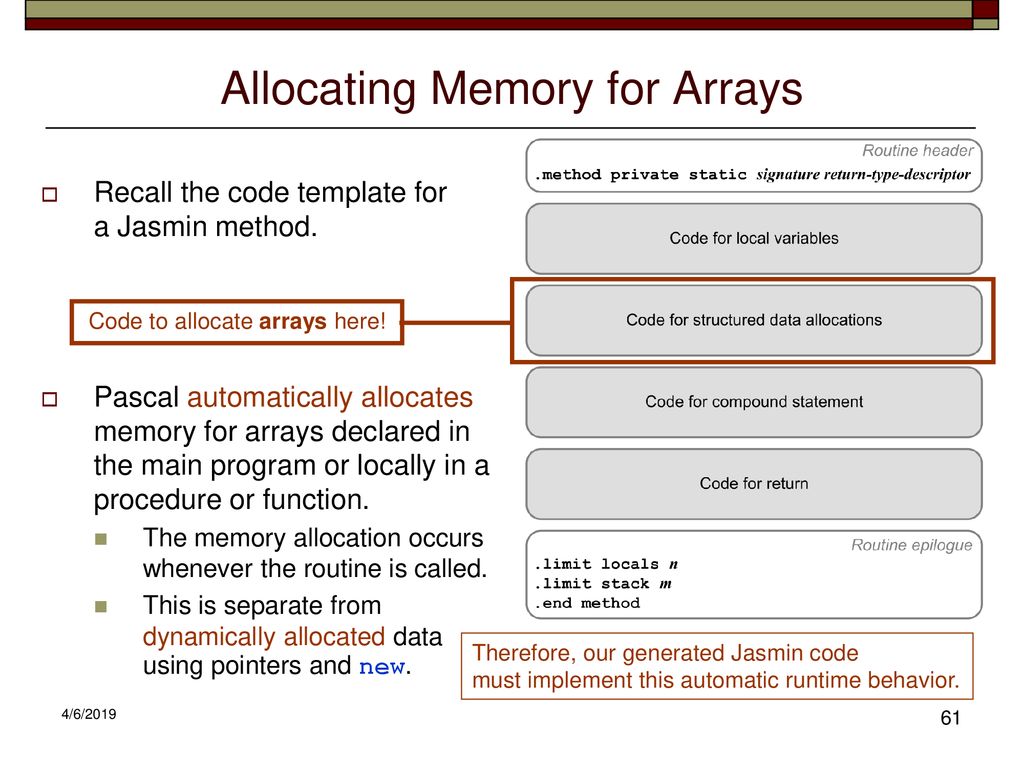
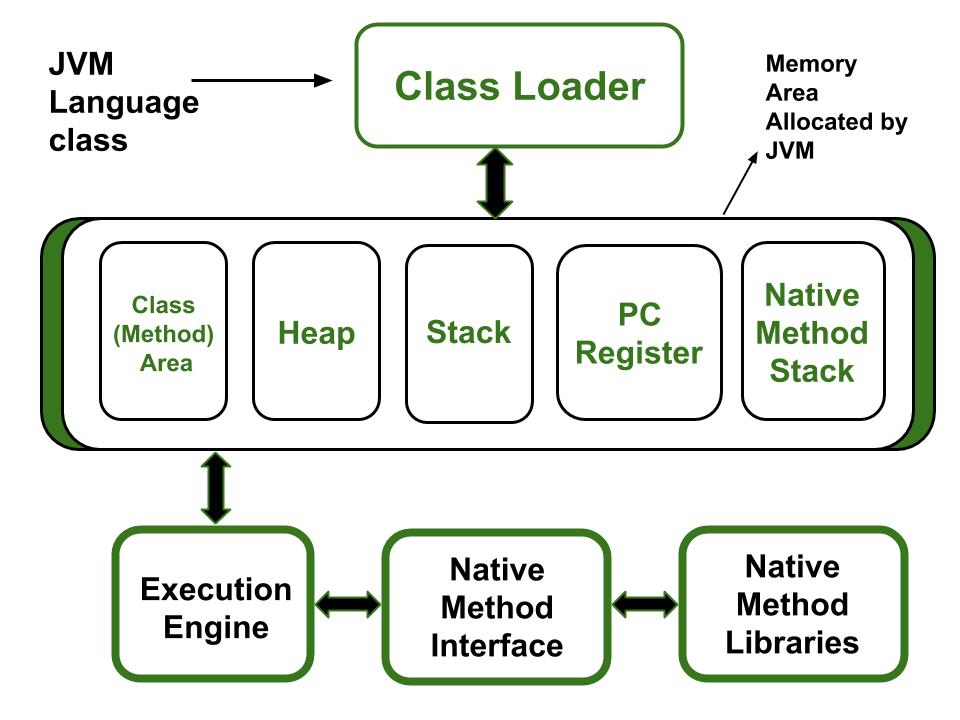
Java Allocate Memory For Template Array - In this tutorial, we’re going to see how the jvm lays out objects and arrays in the heap. Objects are created with the help of “new” keyword and are allocated in the heap memory. At first, all these references just point to null objects. Then, we’ll explore the different object and array. Heap allocation, garbage collection, and performance impacts. Using java.util.arrays.copyof(string[]) is basically doing the same thing as: Arrays are continuous space of memory, so they look like more your first sketch: Learn java’s array memory management essentials: Java handles memory allocation for arrays in two main. If (wordlist.length == wordcount) { string[] temp = new string[wordlist.length + arraygrowth];. However, declaring a variable of a class type does not create an object it only. Then, we’ll explore the different object and array. Learn java’s array memory management essentials: At first, all these references just point to null objects. When you write code, every variable, object, or class requires memory to function. Heap allocation, garbage collection, and performance impacts. In short, when you create the array of objects, you really create an array of references. How is the memory allocated(stack and heap reference) when an object array is created? Creating an array of 100,000,000 used 12,512 bytes of heap and took 1.8 seconds to set and. First, we’ll start with a little bit of theory. When you write code, every variable, object, or class requires memory to function. When you do staff[0] = new. Heap allocation, garbage collection, and performance impacts. How is the memory allocated(stack and heap reference) when an object array is created? Objects are created with the help of “new” keyword and are allocated in the heap memory. First, we’ll start with a little bit of theory. Objects are created with the help of “new” keyword and are allocated in the heap memory. Java handles memory allocation for arrays in two main. Using java.util.arrays.copyof(string[]) is basically doing the same thing as: When you write code, every variable, object, or class requires memory to function. Java handles memory allocation for arrays in two main. Heap allocation, garbage collection, and performance impacts. Using java.util.arrays.copyof(string[]) is basically doing the same thing as: At first, all these references just point to null objects. In short, when you create the array of objects, you really create an array of references. At first, all these references just point to null objects. //declaring array intarray = new int[10]; First, we’ll start with a little bit of theory. If (wordlist.length == wordcount) { string[] temp = new string[wordlist.length + arraygrowth];. Learn java’s array memory management essentials: At first, all these references just point to null objects. Heap allocation, garbage collection, and performance impacts. If (wordlist.length == wordcount) { string[] temp = new string[wordlist.length + arraygrowth];. When you do staff[0] = new. Using java.util.arrays.copyof(string[]) is basically doing the same thing as: Creating an array of 100,000,000 used 12,512 bytes of heap and took 1.8 seconds to set and. Objects are created with the help of “new” keyword and are allocated in the heap memory. At first, all these references just point to null objects. When you do staff[0] = new. Memory allocation in java is the backbone of its efficiency and. If (wordlist.length == wordcount) { string[] temp = new string[wordlist.length + arraygrowth];. Using java.util.arrays.copyof(string[]) is basically doing the same thing as: Learn java’s array memory management essentials: In short, when you create the array of objects, you really create an array of references. In this tutorial, we’re going to see how the jvm lays out objects and arrays in the. //declaring array intarray = new int[10]; Using java.util.arrays.copyof(string[]) is basically doing the same thing as: Creating an array of 100,000,000 used 12,512 bytes of heap and took 1.8 seconds to set and. Arrays are continuous space of memory, so they look like more your first sketch: At first, all these references just point to null objects. When you do staff[0] = new. When you write code, every variable, object, or class requires memory to function. Creating an array of 100,000,000 used 12,512 bytes of heap and took 1.8 seconds to set and. In short, when you create the array of objects, you really create an array of references. If (wordlist.length == wordcount) { string[] temp =. Arrays are continuous space of memory, so they look like more your first sketch: First, we’ll start with a little bit of theory. Then, we’ll explore the different object and array. If (wordlist.length == wordcount) { string[] temp = new string[wordlist.length + arraygrowth];. Objects are created with the help of “new” keyword and are allocated in the heap memory. However, declaring a variable of a class type does not create an object it only. Memory allocation in java is the backbone of its efficiency and reliability. When you write code, every variable, object, or class requires memory to function. //declaring array intarray = new int[10]; Objects are created with the help of “new” keyword and are allocated in the heap memory. Heap allocation, garbage collection, and performance impacts. Creating an array of 100,000,000 used 12,512 bytes of heap and took 1.8 seconds to set and. When you do staff[0] = new. In short, when you create the array of objects, you really create an array of references. At first, all these references just point to null objects. Arrays are continuous space of memory, so they look like more your first sketch: Then, we’ll explore the different object and array. In this tutorial, we’re going to see how the jvm lays out objects and arrays in the heap. Using java.util.arrays.copyof(string[]) is basically doing the same thing as: Java handles memory allocation for arrays in two main.Memory Allocation in Java How Does Memory Allocation work in Java?
Java Memory Allocation.
CS 432 Compiler Construction Lecture ppt download
Java Stack and Heap Memory Studytonight
Comparing Memory Management In Java And C
java memory allocation , stack and heap Stack Overflow
Java JVM Memory Hoomels
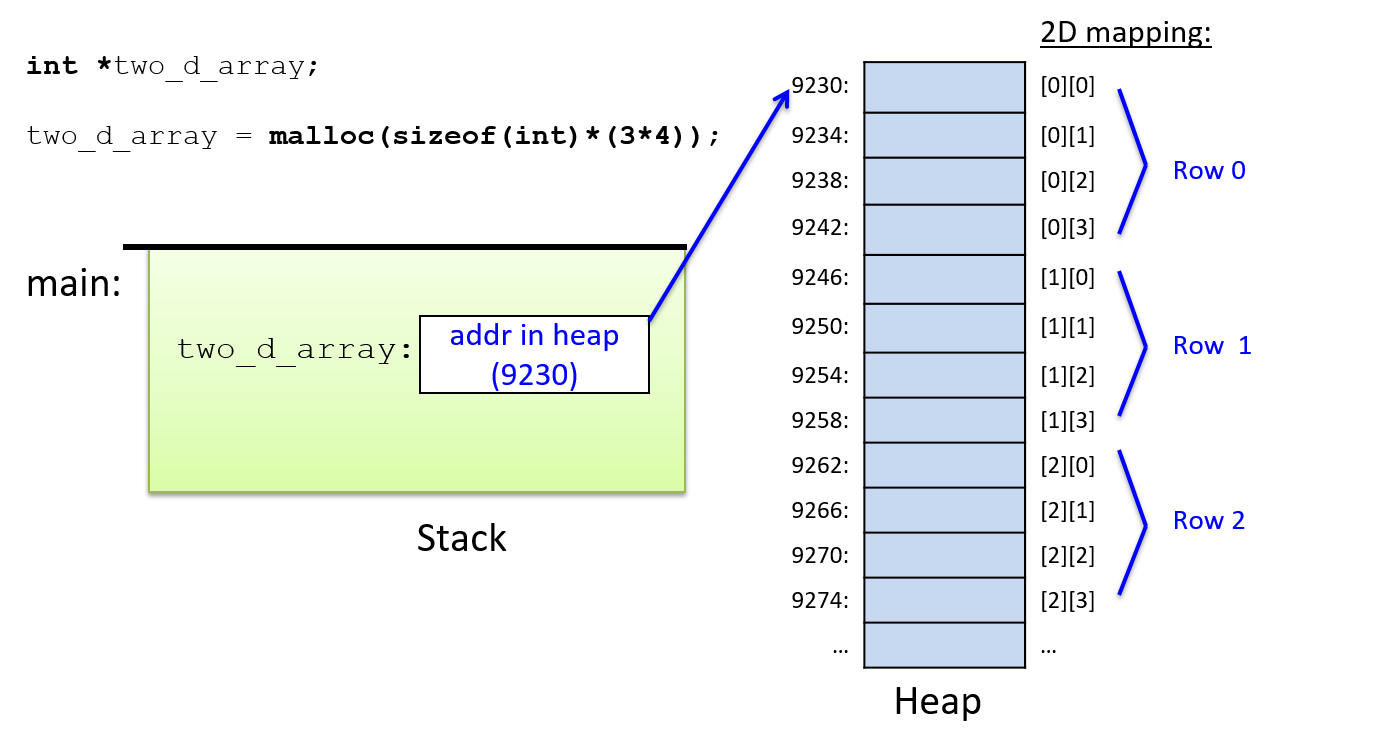
Dive Into Systems
73. Dynamic Memory Allocation in One Dimensional Array Java Programming
String Memory Allocation in Java (Stack Memory Vs Heap Memory Vs String
First, We’ll Start With A Little Bit Of Theory.
Learn Java’s Array Memory Management Essentials:
How Is The Memory Allocated(Stack And Heap Reference) When An Object Array Is Created?
If (Wordlist.length == Wordcount) { String[] Temp = New String[Wordlist.length + Arraygrowth];.
Related Post: